How briskly trend can lower its staggering environmental impression


Quick trend ends in new strains being added each week — as an alternative of 4 occasions a yr — most of which fits to landfill.Credit score: Eve Edelheit/Bloomberg/Getty
Garments had been as soon as used till they fell aside — repaired and patched to be re-used, ending their lives as dishcloths and oil rags. Not right now. In high-income nations particularly, clothes, footwear and upholstered furnishings are more and more ceaselessly purchased, discarded and changed with new fashions, that are themselves quickly discarded and changed.
The proof is there within the knowledge. In 1995, the textiles business produced 7.6 kilograms of fibre per individual on the planet. By 2018, this had almost doubled to 13.8 kilograms per individual — throughout which period the world’s inhabitants additionally elevated, from 5.7 billion to 7.6 billion individuals. Greater than 60 million tonnes of clothes is now purchased yearly, a determine that’s anticipated to rise nonetheless additional, to round 100 million tonnes, by 2030.
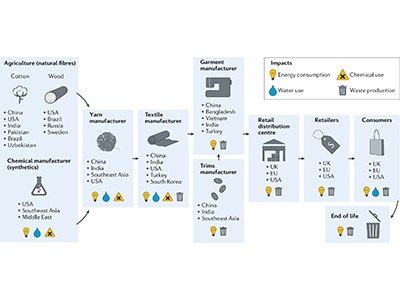
‘Quick trend’ is so known as partly as a result of the style business now releases new strains each week, when traditionally this occurred 4 occasions a yr. At present, trend manufacturers produce virtually twice the quantity of clothes that they did in 2000, most of it made in China and different middle-income nations resembling Turkey, Vietnam and Bangladesh. Worldwide, 300 million individuals are employed by the business.
However extremely, greater than 50 billion clothes are discarded inside a yr of being made, based on a report from an knowledgeable workshop convened by the US Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST), revealed in Might.

Landmark treaty on plastic air pollution should put scientific proof entrance and centre
Textiles match into two broad classes: pure and artificial. The manufacturing of these resembling cotton and wool, that are produced from plant and animal sources, is basically secure, albeit slowly rising. Against this, the manufacturing of polymer-based fibres, notably polyester, raced forward from about 25 million tonnes a yr in 2000 to some 65 million tonnes in 2018, based on the NIST workshop report. Taken collectively, these developments are having a staggering environmental impression.
Take water. The style business, one of many world’s largest customers of water, consumes wherever from 20 trillion to 200 trillion litres yearly. Then there are microplastics. Plastic fibres are launched once we wash polyester and different polymer-based textiles, and make up between 20% and 35% of the microplastics choking the oceans. Added to this are particular chemical substances, resembling these used to make materials stain resistant and the pesticides required to guard crops resembling cotton.
Change is sorely wanted, however would require the style business to work more durable to embrace extra of what’s often called the round financial system. That may contain not less than two issues: refocusing on making issues that final, and so encouraging reuse; and extra quickly increasing the applied sciences for sustainable manufacturing processes, particularly recycling. There’s an enormous position for analysis — each educational and industrial — in attaining these and different ambitions.
Researchers might start by serving to to supply extra correct estimates of water use. It should absolutely be attainable to slender the vary between 20 trillion and 200 trillion litres of water. There may be additionally work to be carried out on bettering and increasing textiles recycling. Overwhelmingly, used textiles go to landfill (in the USA, the proportion is round 85%), partly as a result of there are comparatively few programs (at scale) that accumulate, recycle and reuse supplies. Such recycling requires the handbook separation of fibres, in addition to buttons and zippers. Completely different fibres are usually not simple to determine by eye, and general such handbook processes are time-consuming. Equipment is being developed that may assist. Applied sciences additionally exist to recycle used fibres chemically and to create high-quality fibres that may be reused in clothes. However these are nowhere close to the size wanted.
One other problem for researchers is to work out the right way to get shoppers and producers to alter their behaviour. That is already an lively space of examine within the social and behavioural sciences. For instance, Verena Tiefenbeck at Bonn College in Germany and her colleagues discovered that when lodge company had been proven real-time suggestions on the power utilized in having a shower, it lower down power consumption from showering by 11.4%1. Different analysis questions embrace discovering methods to encourage individuals to buy sturdy items; exploring the right way to fulfill cravings for one thing new whereas decreasing environmental impression; and understanding why sure interventions may be efficiently scaled up whereas others fail.
The environmental worth of quick trend
Business and academia might additionally collaborate to ascertain a system to trace textile microplastics. This may very well be carried out digitally, for instance. It will require an agreed definition of what constitutes textile microplastics, resembling their materials composition and dimensions. Corporations, universities, campaigners and governments additionally want to contemplate the right way to make their applied sciences extra accessible. Doing so would speed up improvement and testing, and (ultimately) adoption at scale.
There are additionally schemes in different fields that may very well be a supply of concepts. The World Well being Group has appreciable expertise the place accessibility is anxious, for instance, in its Entry to COVID-19 Instruments Accelerator. By way of this, corporations and governments agree the ideas of sharing key applied sciences in diagnostics and drug improvement. And within the early 2000s, the Rockefeller Basis, underneath its then-president Gordon Conway, an ecologist now at Imperial Faculty London, made an enormous push to encourage corporations to share applied sciences in agricultural biotechnology, by establishing the African Agricultural Know-how Basis. These schemes are usually not excellent and are regularly evolving, however supply concepts and classes that ought to be studied and regarded.
Within the meantime, marketing campaign teams are doing a lot of the heavy lifting with business. The Ellen MacArthur Basis, a UK-based charity that promotes circular-economy options, is within the second iteration of a marketing campaign known as the Denims Redesign, which challenges clothes producers to give you round options to that stalwart of each wardrobe. Some producers have made their jeans-production course of extra round through the use of natural cotton, and by inserting zips in a method that enables them to be simply eliminated when garments are recycled. Others are utilizing strengthened stitching to make their merchandise last more. These are vital proofs of precept, however such strategies must develop into mainstream.
These actions come at a price and problem the concept of quick trend, as a result of they may make objects much less reasonably priced to shoppers seeking to sustain with newest developments. Manufacturers and retailers take a critical view on dangers to their backside line (and may select to delay motion on sustainability in consequence). For this reason authorities motion is essential.
Insurance policies want precision and tooth, which present ones don’t at all times have, and may, ideally, be coordinated. A advice from the European Union for member states, for instance, says that by 2030 there have to be “necessary minimums for the inclusion of recycled fibers in textiles, making them longer-lasting, and simpler to restore and recycle”. That is too imprecise. With out extra particular targets it is going to be very tough to trace for compliance functions. China, the world’s largest textiles producer, additionally has a five-year circular-economy plan for the business. Contemplating quick trend’s interconnectedness, China and the EU, along with the USA and others, should strive more durable to coordinate their efforts.
Small steps are good, however massive modifications are wanted. There’s no time to waste in the case of altering textiles manufacture and design. The shameful environmental value of a whizzy new wardrobe must be tackled instantly, at scale, with model and panache.